|
|
|
- Contact
us Other instruments: - Measures
-
Scales |
|
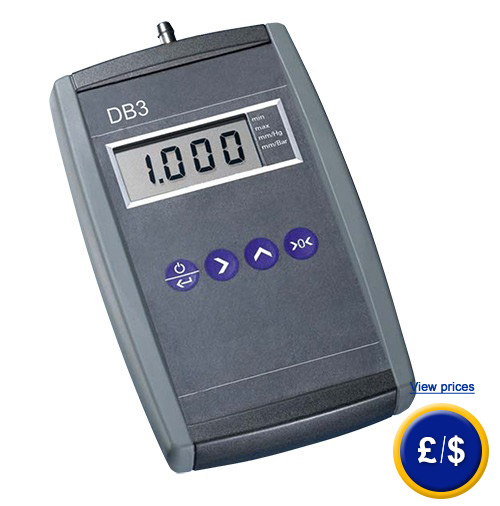
Barometer PCE-DB 3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Barometer DB 3 is an ideal device for measuring absolute pressure. It is equipped with a scalable analogue output. The atmospheric pressure measured by the barometer indicates the weight of the air (atmosphere) according to the gravity of the earth. At sea level the barometer marks a value of 1013.25 mbar in stable conditions (isothermal atmosphere). The barometer is delivered with a barometric pressure of 1013 mbar at sea level. Changes in altitude must be taken into account when measuring the absolute pressure. The barometer digital display shows the current atmospheric pressure (depending on weather conditions and altitude). It often takes that value as a correction factor for the barometer to measure accurately. Due to the built-in differential pressure measurement, you can see changes in weather or altitude. For this, the barometer is set to zero with the current barometric pressure. Later changes are shown; the barometer goes "up" or "down." For example, while going up in a tall building you see the difference in altitude of the barometer on the screen. If you have any questions about the barometer, see the following technical data or contact us: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
- High accuracy |
- Measurement of the pressure - Zero value correction - Factory calibration or DKD calibration optional - 4-digit LCD display - Calculation of average in oscillating values - Automatic shut-off after 20 minutes - Measurement pause |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Barometer PCE-DB 3 as a vacuum gauge or pressure |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Technical specifications for the PCE-DB 3 barometer |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
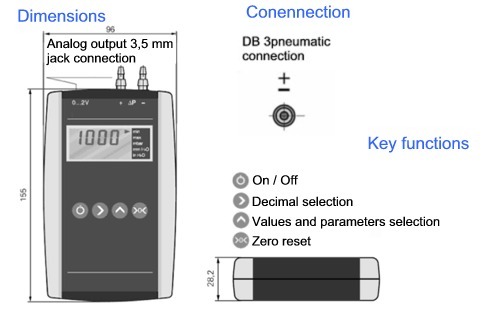
Dimensions of the PCE-DB 3 barometer |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Delivery content: 1 x barometer DB 3, 1 x user manual. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Delivery content: - Certificate of factory or DKD certificate |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ISO calibration and certification of the barometer An ISO calibration certificate can be acquired for this barometer. In a laboratory certification and calibration for the ohmmeter, a certificate of control is issued with the details of your company so you can register the devices in their intra-corporate consortia ISO control instruments. In this document, it is also certified that such devices may again be adjusted according to the national standards. Below you will find more information on calibration. • Performance of the measuring instruments This means that the user is responsible for checking and controlling the interval between calibrations. This calibration interval should be between 1 and 3 years. We also offer the user our expert advice in solving any problem related to the process of establishing calibration intervals or any other technical questions. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
What is pressure? Pressure can be defined as the physical quantity expressing the force exerted by one body on the surface of an area, where in most cases it is directly measured by its balance with another force, such as liquid column, a spring, a piston loaded with weights or any other element that can undergo deformation when pressure is applied. The unit in which pressure is measured is the Pascal. P = F/A We distinguish various types of pressure: - Absolute pressure: the pressure of a fluid with reference to a perfect vacuum or absolute zero. Absolute pressure is zero only when there is no clash between the molecules indicating that the proportion of molecules in the gaseous or molecular velocity is very small. This term was created because the atmospheric pressure varies with altitude and often devices made in other countries at different altitudes above sea level have other atmospheric pressures. This term unifies all criteria. We also have another model of the barometer to measure absolute pressure. - Atmospheric or relative pressure: the weight of the air in the atmosphere exerts pressure on a particular point on the surface of the earth. Generally, the more air above an area, the higher the pressure, which means that atmospheric pressure varies with altitude. For example, atmospheric pressure is greater at the sea level than at the top of a mountain. To compensate the difference and to facilitate comparison between various locations with different altitudes, atmospheric pressure is usually adjusted to the equivalent of the sea level (barometric pressure). This barometer can measure atmospheric pressure. - Barometric pressure: the atmospheric pressure is usually adjusted to the equivalent sea level. The barometric pressure varies with weather conditions - therefore it is an essential tool for weather forecasts. For example, with the barometer at your disposal, you would have no problem performing the measurement of barometric air pressure. This barometer is an altimeter. As you ascend in altitude, the atmospheric pressure decreases. This device is used to calibrate the altimeter and the weather station for weather forecast. - Gauge pressure is the force that the weight of the column of atmosphere above the measuring point exerts per unit area. The unit of measurement of the gauge pressure in the metric system is the hectoPascal (hPa) corresponding to a 100 Newton (N) on a square meter. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Below is a conversion table which will allow you to quickly determine the range of pressure in your place of work, in distinct units of measurement normally used to measure pressure. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Here you will find an overview of all measuring instruments available at PCE Instruments. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Contact: |
Contact: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||























































