|
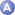 A-weighting
A-weighting
The sensitivity of human hearing
depends on the frequency. Low and high tones are perceived with less
precision than the tones in between. In the measurement of noise or
sound this is taken into account and the frequencies contained
within the sound are valued differently with respect to the A-weighting
curve.
Sound
readings are taken in decibels (dB) (A). The A-weighting curve is
used primarily in the environmental and industrial sectors; the B
and C curves are used for louder sounds and are less frequently
used. The noise analysers most commonly used for these measurements are the
PCE-999
and the
PCE-322A.
 Decibel
Decibel
The decibel
consists of one tenth of a bel (B). A bel is defined as a logarithm
of the bahaviour of two readings of the same type. It is used for the measurement of sound levels although the actual
sound output is determined in relation to a specified reference
intensity
Abbreviation: dB.
Calculation: LP = 10 * log (P / P0)
in dB
where
P = sound output
P0 = specified reference
intensity (typically, 10 - 12 Watt)
 Equivalent continuous noise level
(Leq)
Equivalent continuous noise level
(Leq)
The equivalent
continuous noise level is an energy mean of the noise level averaged
over the measurement period (T) and often regarded as an average
level.
Its also part of a sound level over a duration of time (X)
that describes a noise with duration D has the same value as a noise
that has half the duration (D / 2), but for this it has a sound
level of 3dB ( = 10 * log 2) higher
(to take this measurement you require the
PCE-353
noise analyser.)
The Leq is calculated in this way:
Leq = q/log2 * log(1/T ( 10(log2/q)* Li * ti)
Li = unique event level
T = period of measurement (for
example: 16 hours),
ti = duration of the unique event, the
maximum level can't be increased by more than 10dB,
q =
equivalence parameter or division by two. Provides the change of
level, that is equivalent to a constant level to duplicate or divide
by two the effective time. Normally at international level q=3,
corresponding to the energy equivalence.
Regular measurment
of chance occurances with constant intervals
(example, 1/10 or 1/100 s) the value can be occur analogically
to the number of the chance value
Leq = q/log2 * log(1/N ( 10 (log 2/q)* Li)
where
Li = value of chance occurance
N = total number of
chance occurances over a period of measurment.
The sound level of
extended duration with equivalent energy used for acoustic
description of different sources of environmental noise (noise
from planes, trains, etc.) In Germany the Leq is normally know as the level
median (Lm).
 Infrasound
Infrasound
Frequencies
below 16 Hz (Hz = 1/s)
 Level day-evening-night
(Lden)
Level day-evening-night
(Lden)
According to the
proposed directives of the EU relating to "Measurement and treatment
of environmental noise" for the index of produced noise: day/evening/night
level. The evening hours are 19:00 to 23:00
o'clock, with a supplement of 5dB and at night from 23:00 to 7:00
o'clock, with a supplement of 10dB (for example, the noise analyser
serie-1900.)
Ldn
Day-night average sound level is the average noise level over a 24
hour period. With it, different measurements can be taken at
different times of the day.
 Maximum level
Maximum level
Maximum value is a sound event also denoted as a peak sound. In
sound bursts, it's easier todetermine various peak pints and
establish a maximum average or extract the L1 percentile level.
Measurement level
The
measured sound level calculated over a period of time in a
measurement of noise which has certain noise level specifications be
means of noise level corrections. For these measurements it is
advised to use noise analysers with the
Frequency
analysis
function.
Abbreviatons: RL (rating level),
during daytime (LT); during nightime (LN) (in dB).
In American
English it is also referred to as Ldn frequency.
 Peak level
Peak level
Maximum sound
level reached in a sound burst, also called maximum level. Because
of possible loud oscillations, it provides a better description of
the average maximum level or the L1 percentile level.
 Solid bodies
Solid bodies
Sound that
spreads and impacts with solid bodies such as ceilings and walls of
buildings. This has high importance in the noise produced by the
construction sector.
Sound pressure level
The magnitude of sound pressure of a source (px) relative to a level
reference sound pressure (p0). L = 20 log (px/p0). It is expressed
in decibels (dB), almost always compared with frequency value, for
example, dB (A).
Sound energy
The physical energy of a source of radiated sound.
Sound event level (SEL)
(also LAE). Parameter largely related to the LAeq. With it isolated
events can be determined
(for example, air transit or passing traffic). The sound
energy is normalized to a temporary duration of 1 second.
Sound TA
Technical
indication for the protection against noise
General prescription
administered by the Federal emissions law 26.8.98. In ruido TA value
directives are determined that should be followed precisely to
protect the public from the harmful effects of noise. Ruido TA has
advanced in force to be used for installations with authorization
and for those that don't require authorization.
 Temporary value
Temporary value
To be
able to follow oscillating sound levels in display instruments that
were previously constant, different temporary constants are
introduced: Fast, Slow, Impulse. Normally the temporary value that
you should employ is prescribed.
Sound bursts are considered to
have a more imbalanced frequency than sounds events of longer
durations. For this reason, it has to be taken into account in the
reading, the duration of the bursts by way of a temporary value. (source: UBA).
Guide lines
for the measurement of sound /
noise:
1. Standard immission values
Roads and
Trains - Sound prevention
Standard immission values in dB (A)
|
Place
|
day (6 - 22 hours)
|
night (22 - 6 hour)
|
|
hospitals, schools,
spas and resting places
|
57
|
47
|
|
residential centre
|
59
|
49
|
|
town centers, towns
and mixed zone
|
64
|
54
|
|
industrial areas
|
69
|
59
|
2. Standard immission
values Streets -
Noise sanitation
Standard immission values in dB (A)
|
Place
|
day (6 - 22 hours)
|
night (22 - 6
hours)
|
|
hospitals, schools,
spas and dwelling for the elderly residential areas
|
70
|
60
|
|
town centers, towns
and mixed zone
|
72
|
62
|
|
industrial areas
|
75
|
65
|
3. Standard immision
values for Airborne noise
Standard immission values in dB (A
|
Place / Zone
|
|
Protection zone 1 Leq >= 75
|
|
Protection zone 2 67 <= Leq < 75
|
4. Standard
immision values fo
Industrial noise
Standard immission values in dB (A
|
Place
|
day (6 - 22 hours)
|
night (22 - 6 hours)
|
|
a)
in industrial areas
|
70
|
70
|
|
b)
in professional activity areas
|
65
|
50
|
|
c)
town centers, towns and mixed zone
|
60
|
45
|
|
d)
residential areas
|
55
|
40
|
|
e)
residential areas
|
50
|
35
|
|
f)
spas, hospitals and dwelling for the elderly
|
45
|
35
|
The night-time can vary one hour if it is necessary
because of specifications of the living-place or working conditions
paying attention to protect against environmental
harmful effects. A rest at night of eight hours should
be guaranteed.
Short isolated sound ends should not exceed immission
values over 30dB (A) at day-time and 20 dB (A) at
night-time.
For transference of sounds inside buildings and immision
values for those areas that need protection against
sound except for industrial areas, the DIN 4109 standard
dated from November 1989 classifies sound areas from a
to f.
Day 35 dB (A) night 25 dB (A)
Short isolated sound ends will not exceed immision
values of 10 dB (A).
Special events
For special sound events, outdoors immission values will
be within the areas from b t f.
day 70 dB (A) night 55 dB (A)
Short isolated sound ends should not exceed immision
values of table 1 part b, 25dB (A) at day-time and 15 dB
(A) at night-time. For table 1 c and f these values will
be 20 dB (A) at day-time and 10 dB (A) at night-time.
Immision values at day-time are valid for 16 hours. At
night, a complete hour is determined (for instance from
1.00 to 2.00 hours) with the highest value.
Additions for high sensitivity hours at day-time
The table part from d to f must be considered to
determine sound immission values and harmful effects.
1. Working days
06.00 - 07.00 hours, 20.00 - 22.00 hours
2. Sundays and holidays
06.00 - 09.00 hours, 13.00 - 15.00 hours, 20.00 - 22.00 hours.
5. Standard
immision values for
noise in building sites
Standard
immision values dB (A)
|
Place
|
day (7 - 20 hours)
|
night (20 - 7
hours)
|
|
Spas, hospitals
and dwellings for the elderly
|
45
|
35
|
|
exclusively
residential areas
|
50
|
35
|
|
residential areas
|
55
|
40
|
|
residential areas
with professional activities,
|
60
|
45
|
|
areas dedicated
mostly to professional activities
|
65
|
50
|
|
industrial areas
with professional activity where the owner's
houses or manager's houses are placed as well as
the company supervisory board.
|
70
|
70
|
6. Standard
immision values for Noise in sports
Standard
immision values dB (A)
|
Place
|
day (6 - 22 hours)
|
night (22 - 6 hours)
|
|
Spas, hospitals
and dwellings for the elderly
|
45
|
35
|
|
exclusively
residential areas
|
50
|
35
|
|
residential areas
|
55
|
40
|
|
residential areas
with professional activities,
|
60
|
45
|
|
areas dedicated
mostly to professional activitiesl
|
65
|
50
|
Attention: Specifications and values
have been taken from the publications of diverse authors
so these details do not pretend to be exhaustive or
correct.
The text of noise TA in German can be found at the
following link: http://www.umweltrecht.de/recht/laerm/tlaer1.htm
|
















































